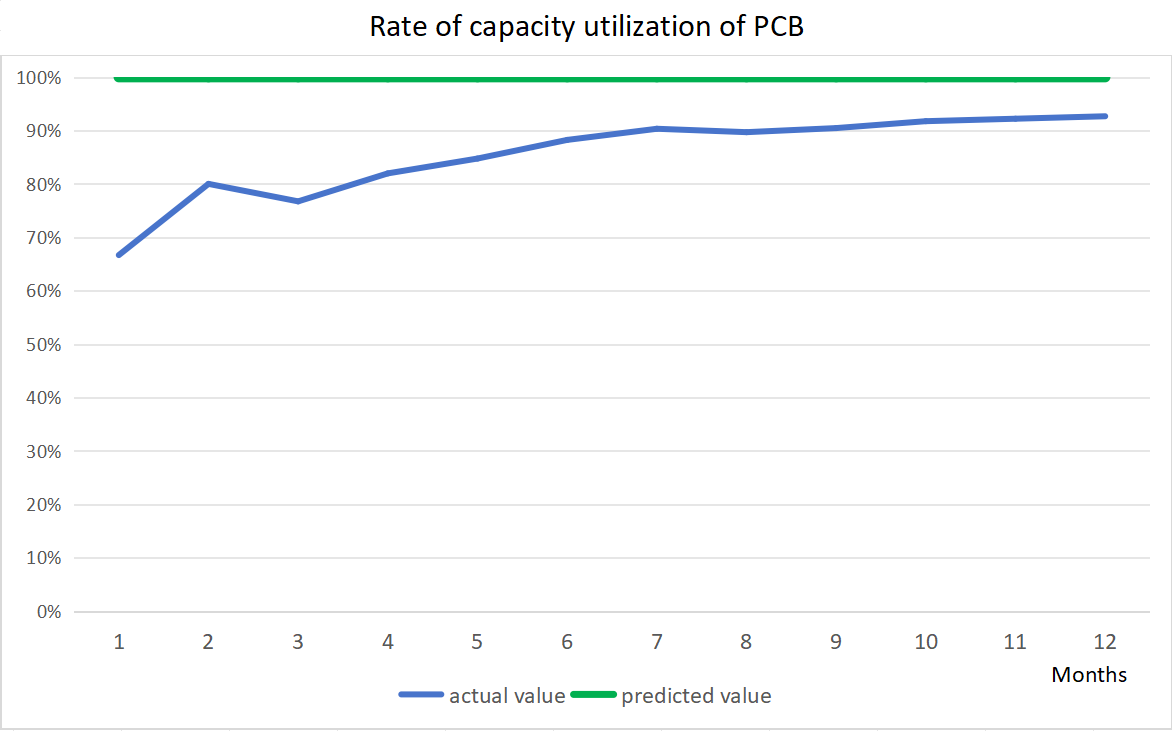
In PCB (Printed Circuit Board) manufacturing, capacity utilization can be measured using specific metrics and approaches tailored to the nature of PCB production. Here are some methods to measure capacity utilization in PCB manufacturing:
1.Production Output vs. Maximum Capacity: Compare the actual number of PCBs produced to the maximum capacity of the production line or facility. This can be calculated using the formula:
Capacity Utilization=Actual PCB OutputMaximum Capacity×100%Capacity Utilization=Maximum CapacityActual PCB Output×100%
For example, if a PCB manufacturing line has the capacity to produce 10,000 PCBs per day, but it only produces 8,000, the capacity utilization would be 80%.
2.Cycle Time Analysis: Analyze the time it takes to complete a PCB manufacturing process from start to finish. Compare this cycle time with customer demand or production targets to assess capacity utilization. Longer cycle times relative to demand may indicate underutilization.

3.Equipment Efficiency (e.g., SMT Machines): Evaluate the efficiency of specific equipment, such as Surface Mount Technology (SMT) machines. Utilize metrics like OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) to assess the effectiveness of these machines in placing components on PCBs.

4.Bottleneck Analysis: Identify the stages in the PCB manufacturing process where production is limited. This may be a specific machine or process step that is consistently operating at or near maximum capacity.
5.Resource Utilization: Monitor the usage of critical resources like machines, labor, and materials. Ensure that machines are operating efficiently and that labor is utilized effectively.

6.Defect Rate and Rework: Analyze the rate of defects in the PCBs produced. High defect rates may indicate issues with the production process, potentially leading to lower capacity utilization due to rework and repairs.

7.Lead Time vs. Customer Demand: Compare lead times (the time it takes to fulfill a customer order) with customer demand. Long lead times relative to demand may indicate underutilization.
8.Inventory Levels: Evaluate the level of raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished goods inventory. Excessive inventory levels may suggest overproduction and underutilization of capacity.
9.Employee Productivity: Track the productivity of workers in terms of PCBs assembled or processed per hour or per shift.
10.Yield Rate: Assess the yield rate, which is the ratio of good PCBs produced to the total PCBs manufactured. A low yield rate may indicate inefficiencies in the production process.
It's important to note that these methods can be used individually or in combination to provide a comprehensive view of capacity utilization in PCB manufacturing. Additionally, implementing a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) can provide real-time data and analytics to monitor and optimize capacity utilization.
Contact: Ella Ouyang
Phone: 86-13570888065
Tel: 86-0755-28632299
Email: ellaouyang@szxpcba.com
Add: Building 8, Gangbei Industrial Zone, Huangtian, Xixiang, Bao’an District, Shenzhen, China.
We chat